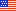
Federal Bureau of Prisons

- Director Bureau of Prisons
- Commissioner, Federal Prison Industries
- Chief of Staff
- Federal Prison Industries, Inc. - Board of Directors
- Federal Prison Industries, Inc.
- National Institute of Corrections - Advisory Board
- National Institute of Corrections
- Deputy Director
- Office of Congressional and Public Affairs
- National Institute of Corrections
- General Counsel and Review
- Health Services Division
- Correctional Programs Division - Assistant Director
- Reentry Services Division
- Regional Offices - Regional Directors
- Mid-Atlantic
- North Central
- Northeast
- South Central
- Southeast
- Western
- Field Operations
- Associate Deputy Director
- Administration Division
- Information Technology and Data Division
- Human Resource Management Division
- Program Review Division
Approved by: Merrick B. Garland, Attorney General
Date: February 18, 2022
The Federal Bureau of Prisons (BOP) was created by the Act of May 14, 1930 (ch.274, 46 Stat. 325), signed into law by President Herbert Hoover.
The mission of the BOP is to protect society by confining offenders in the controlled environments of prisons and community-based facilities that are safe, humane, cost-efficient, and appropriately secure, and that provide work and other self-improvement opportunities to assist offenders in becoming law-abiding citizens.
The major functions of BOP are to:
- Proactively manage the offender population to ensure safe and secure operations.
- Provide services and programs to address inmate needs, provide productive use-of-time activities, and facilitate the successful reintegration of inmates into society, consistent with community expectations and standards.
- Ensure there is a competent, diverse workforce operating within a professional work environment to meet the current and future needs of the organization.
- Maintain all BOP facilities in operationally sound conditions and in compliance with security, safety, and environmental requirements.
- Manage operations and resources in a competent and effective manner that encourages creativity and innovation in development of exemplary programs, as well as excellence in maintaining the basics of correctional management. Continually strive toward improvements in effective use of resources and efficient delivery of services.
- Continue to seek opportunities to expand the involvement of community, and local, state, and federal agencies, in improving the effectiveness of the services provided to offenders and constituent agencies. Seek to improve partnerships that will allow the Bureau to carry out its mission within the criminal justice system and to remain responsive to other agencies and the public. Develop partnerships to focus the shared responsibility for the establishment of a supportive environment to promote the reintegration of offenders into the community.
- Provide for public safety and security by focusing on preventing, disrupting, and responding to terrorist activities.
BOP encompasses two subcomponents:
Federal Prison Industries, Inc. (FPI)
The Federal Prison Industries, Inc. (FPI), a wholly-owned government corporation, was created by statute (P.L. 73-461) on June 23, 1934, and implemented by Executive Order No. 6917, signed by President Roosevelt on December 11, 1934.
The mission of the Federal Prison Industries, Inc., is to provide training and employment of prisoners confined in Federal Correctional Institutions.
The major functions of the FPI are to:
- Exercise jurisdiction over industrial enterprises of all Federal Correctional Institutions.
- Maintain a diversified program of industrial operations that ensure optimum inmate employment.
- Provide a wide range of products and services to other federal agencies at fair market prices, structuring product lines to minimize competition with private sector industry and labor in any particular product or service area.
- Provide job skills training and work opportunities for federal prison inmates, maximizing their chances to secure work upon their release, and successfully reenter society as contributing, tax-paying citizens.
- Enhance both staff and inmate security and safety by providing a safe, secure, and meaningful work environment for a substantial number of inmates, keeping them productively engaged and reducing prison idleness.
National Institute of Corrections (NIC)
The National Institute of Corrections (NIC) is a national center that provides assistance to federal, state, and local correctional agencies and works to advance the practice of corrections throughout the country. The NIC was created by statute (P.L. 93-415) on September 7, 1974.
The National Institute of Corrections is a center of learning, innovation and leadership that shapes and advances effective correctional practice and public policy. It works to collaboratively respond to the needs of the corrections field by providing assistance, information, education, and training to correctional agencies.
The major functions of NIC are to:
- Provide assistance to federal, state, and local correctional agencies, and work to advance the practice of corrections throughout the country.
- Provide training, technical assistance, information clearinghouse services, and support promising practices research and implementation, all to reinforce policy formulation to advance correctional practices in prisons, jails, and community corrections agencies.
- Provide leadership to influence correctional policies, practices, and operations nationwide in areas of emerging interest and concern to correctional executives and practitioners as well as public policymakers.
Federal Bureau of Prisons Field Structure
Western Region
WA, OR, CA, NV, ID, MT, WY, UT, AZ, AK, HI
North Central Region
ND, SD, NE, CO, KS, MO, IA, MN, WI, IL, MI, IN
South Central Region
NM, OK, TX, AR, LA
Mid-Atlantic Region
KY, TN, WV, NC, VA, MD, DC, DE
Northeast Region
NY, PA, VT, ME, NH, CT, RI, NJ, OH
Southeast Region
MS, AL, GA, SC, FL, PR, VI
Note - BOP has 6 regions as of May 2012. For additional information on regional operations, see its website.
Click on map for larger version